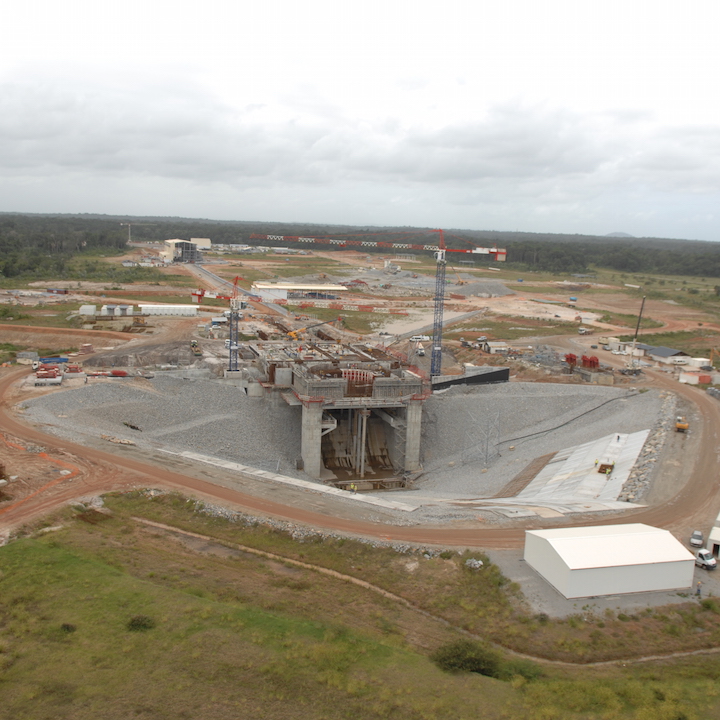
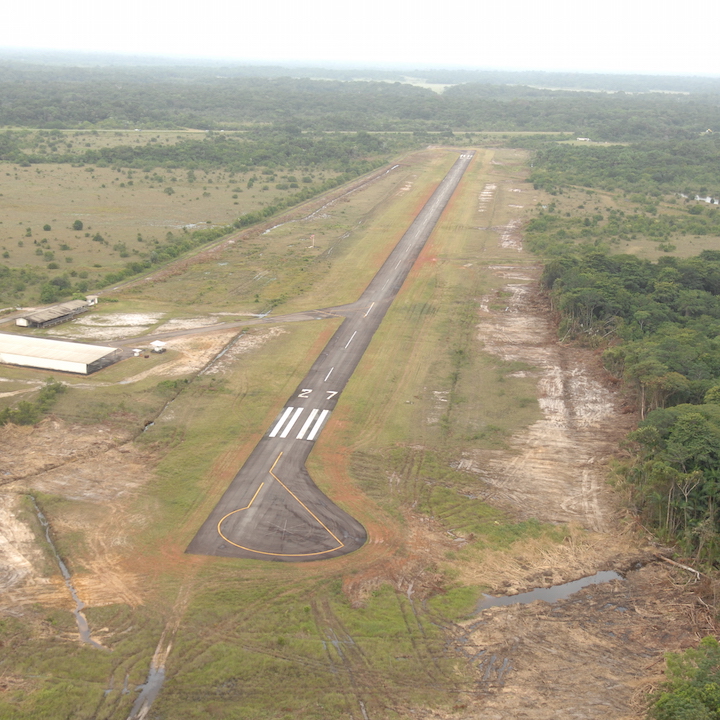
background
In 1962, after Algeria’s independence and the Evian agreements, the Centre national d’études spatiales was forced to leave the Hammaguir launch site. So, 14 other sites were studied to establish a new base. Their special feature was that they were located near the Equator to offer optimal conditions to launch spacecraft. Guiana was chosen for the many advantages it offered. It is easier to manage risks on this sparsely populated territory facing the Atlantic Ocean in case there is a problem with the launcher. The seafront also allows for polar orbit satellites to be launched under optimal conditions. In addition, the zone is not earthquake or cyclone-prone. Finally, Guiana, as an integral French territory, also had the advantage of political stability. That is why, in 2002, following a Franco-Russian agreement, the European Space Agency Council decided to open this Russian Soyuz launcher spaceport here.